Gastric Bypass vs. Gastric Sleeve*
Choose the topic:
Gastric bypass and gastric sleeve are two bariatric surgeries that are performed if a person’s BMI is over 40 or above 35 and if a person suffers from serious health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, infertility and other. If a person suffers from diabetes type 2 mellitus then bariatric surgery can be performed if their BMI is over 30. Both methods are highly effective. However, the techniques, results and potential complications vary considerably.
Performance techniques
Both of these operations are performed laparoscopically. A few minor abdominal incisions are made and laparoscope (a narrow tube equipped with a camera and light) as well as other required instruments are entered to the abdominal cavity.
During gastric bypass surgery the stomach is divided into two parts. A special pouch (stoma) is made in the upper and smaller parts of the stomach. A new pathway is created by cutting through the middle of the small intestine and connecting it to the small pouch formed in the stomach. This procedure makes a bypass of the lower part of the stomach (including pyloric part) and the upper part of the small intestine. The procedure shortens the digestive tract making a person lose a significant amount of weight. The surgery lasts one and a half hour and is performed under general anaesthesia. It usually takes from 2 to 3 months to fully recover.
During the gastric sleeve procedure a surgeon removes three quarters of the stomach. As a result, the stomach takes a shape of a sleeve or tube. The gastrointestinal way remains unchanged. This allows proper absorption of all the consumed food. Gastric sleeve surgery may last up to 2 hours under general anaesthesia. Full recovery after the surgery takes around 2 months.
Advantages of gastric bypass and gastric sleeve
Gastric bypass surgery is very popular because of its efficiency and quick results. Studies show that after gastric bypass people lose about 70 to 80 percent of excess body weight. Due to a decrease in nutrient intake a person starts to defecate more often, on average 3-4 times a day, preventing the body from putting on more pounds. In addition, the pouch formed during the operation is much smaller than the total stomach and this means the patient eats significantly less food. Gastric bypass is a long-term and effective weight-loss treatment. Although gastric bypass is generally considered as a permanent surgery, in rare cases it may be reversed, however restoration of the original integrity of the gastrointestinal tract is a complicated procedure.
Gastric sleeve is also a common surgery. However, it does not produce such an effect as bypass and usually takes the second place in bariatric surgery. There are two main outcomes of this procedure: smaller capacity of the stomach and lower sense of hunger which is caused by removing part of the stomach responsible for production of the hunger hormone ghrelin. It helps a person lose 50-60 percent of the excess body weight. After gastric sleeve surgery the intestinal tract is not changed, digestion occurs naturally, all consumed food is well absorbed. Therefore, there is no risk of losing any nutrients such as iron or calcium. However, a certain diet is still recommended, though it is more flexible than the one recommended after gastric bypass.
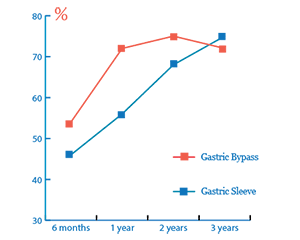
The graphic shows how much excess weight a person loses after Gastric Bypass and Gastric Sleeve on average.
Disadvantages of gastric bypass and gastric sleeve
Although surgeons experienced in bariatric surgery can perform the procedures very quickly and easily, there is still a possibility of complications such as bleeding, infection, formation of thrombus which causes deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolization.
The possible complication specific to gastric bypass is the Dumping Syndromewhich causes diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal discomfort immediately after a meal. This may lead to the fear of eating in public places and other psychological and social problems.
Moreover, after gastric bypass malabsorption may occur. It helps losing extra weight but it also interferes with absorption of important substances (calcium, vitamins, iron) which are essential for one’s body, so extra nutritional supplements should be taken.
Because of gastric bypass characteristics this procedure cannot be performed on patients with ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, anemia, or patients who have a very high level of obesity (BMI over 50 and more).
The main disadvantage of gastric sleeve is the fact that it is a fairly new procedure. As a result, it is less investigated as well as less studied.
Gastric sleeve is irreversible. Moreover, there is a chance to regain the lost weight or to lose only a small amount of weight.
Life after gastric surgery
After any gastric surgery a person has to carefully monitor what he or she eatsfor the rest of their life. Certain food limitations must be followed. For instance, patients will have to cut on high-fat and high-calorie food and sweets. Also the cereals, hard, dry and bulky products, nuts, hard peels of vegetables also should be avoided because of the difficulties related to digestion. People should chew the food well before swallowing, avoid sugary drinks (it causes the dumping syndrome), not to snack between meals, eat protein-rich foods and consume no more than 1,200 calories per day. These rules apply to all weight loss surgeries. The main difference between gastric sleeve and gastric bypass lifestyle wise is that gastric sleeve patients have to take less supplements than gastric bypass ones.
During the first 6 months after gastric bypass about 60 percent of excess weight is lost. Over the next several years weight loss slowly decreases and finally the weight becomes stable. After gastric sleeve surgery weight loss is slower but constant.
Send us your enquiry